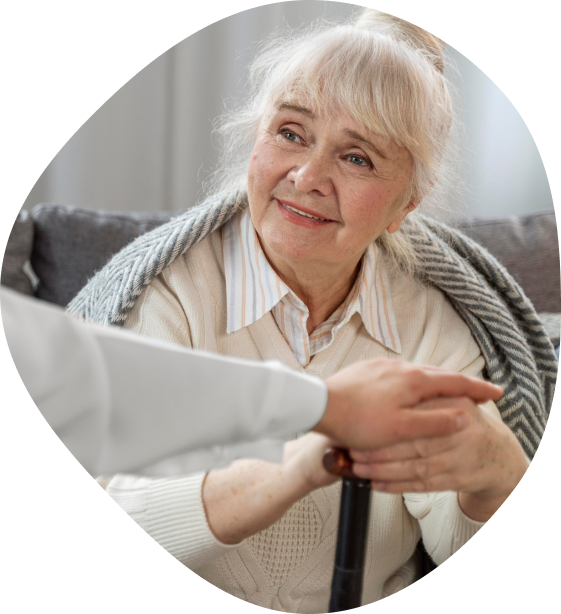
In this guide, we explore the different types of brain injury, how they occur, common symptoms, and the ways they can influence daily life — helping families better understand what to expect and how support can make a difference.
Types of Brain Injury
A brain injury is described as acquired when it occurs after birth and is not related to a congenital condition. Acquired brain injuries can result from a wide range of events, including accidents, medical conditions and illnesses that affect the brain’s normal function.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
A traumatic brain injury is caused by a direct impact or force to the head. This may occur following incidents such as road traffic collisions, falls, assaults or accidents at home or in the workplace.
The impact of a traumatic brain injury can vary greatly from person to person. The severity and long-term effects depend on factors such as where the injury occurred within the brain, the extent of damage and how quickly treatment was received.
Other Forms of Acquired Brain Injury
Not all brain injuries are caused by trauma. Acquired brain injury also includes conditions where damage to the brain occurs due to illness, medical events or internal bleeding. Examples include stroke, brain tumours, infections and oxygen deprivation.
Although the symptoms can be similar to those seen in traumatic injuries, the cause and progression of these conditions often require different treatment approaches and ongoing support strategies.
Common Causes of Acquired Brain Injury
Below are some of the most common conditions that can result in an acquired brain injury:
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Brain damage caused by a blow or force to the head.
Concussion
A mild form of brain injury that can lead to temporary or persistent symptoms, including post-concussion syndrome.
Stroke
A medical emergency that occurs when blood flow to part of the brain is disrupted, resulting in brain tissue damage.
Brain Aneurysm
A weakened blood vessel in the brain that bulges and may rupture, leading to bleeding within the brain.
Brain Haemorrhage
Bleeding in or around the brain, often linked to ruptured blood vessels or severe head injury.
Brain Tumour
An abnormal growth of cells inside the skull that can interfere with brain function.
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Exposure to carbon monoxide can deprive the brain of oxygen, causing hypoxic brain injury.
Encephalitis
Inflammation of the brain, commonly triggered by viral or bacterial infections.
Hydrocephalus
A condition caused by excess fluid within the skull, leading to increased pressure on the brain.
Hypoxic and Anoxic Brain Injury
Damage that occurs when the brain is deprived of oxygen, even for a short period.
Meningitis
An infection that causes inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.





 Our guides
Our guides
